Part 1 of 2.
Governments and businesses in Africa are rapidly developing and modernizing their information system with modern digital technologies.
Kenya leads Africa in the rapid development of fintech and the adoption e-commerce solutions. The government is semi digitized from electronic visas to train tickets, large organizations, insurance companies, financial institutions are all deploying the latest digital infrastructure technologies.
These developments increase attractiveness of The Kenya government and businesses as a lucrative destination for all kinds of cyber-attacks. Currently there exists a huge skill shortage of cybersecurity professionals on the continent to protect the critical assets of governments and private enterprises.
The Kenyan government was amongst the first in the continent to develop and implement a cyber security strategy, Computer Incident Response Team and Coordination Centre and National Digital Forensic laboratory. To achieve Kenyan government goal of safe digital economy the private sector needs to under its overall role in the cyber-hygiene of Kenya digital economy.
Cyber threats, national economic and security challenge
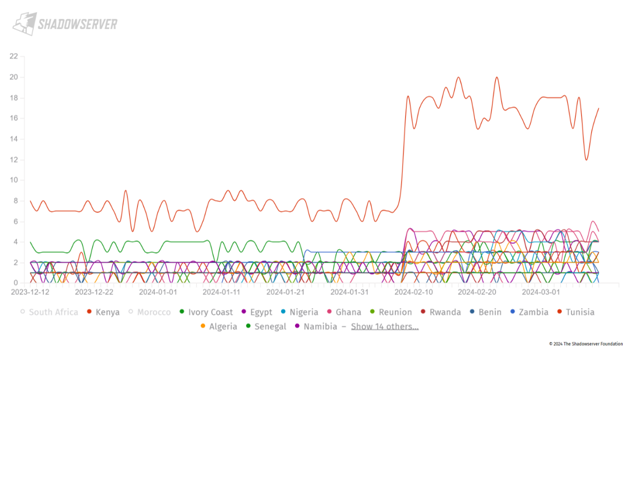
Cyber threat pose a serious national economic and security concerns for Kenya and several African nations. Presently there exist over 11,000 active threat actors operating within Kenya, with the exclusion of those targeting the government and businesses from outside the country. The highest concentration of the threat actors is from Egypt, Algeria, Ethiopia, South Africa, Tunisia, Morocco, and Nigeria.

In the last three months, between January 2024 to March 2024 there has been over 10 000 successful attacks on vulnerable target in Kenya. See Figure 3.

Denial of Service attacks
In Kenya digital landscape today, businesses face a growing threat known as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. These malicious assaults, occurring between February 10th and March 9th, 2024, have impacted businesses and government agencies.
DDoS attacks disrupt normal operations by overwhelming networks or websites with a flood of traffic, making online services inaccessible to legitimate users. This type of cyber threat poses significant challenges to businesses, highlighting the importance of robust cybersecurity measures to mitigate such risks and safeguard against potential disruptions.

Economic Espionage
Economic espionage has emerged as a concerning threat to both the Kenyan government agencies and private enterprises. Over the period spanning from December 22nd to March 1st, 2024, Kenya has faced 20 attempted economic espionage attacks.
These malicious activities, orchestrated by various threats actors, aim to exploit vulnerabilities within organizations, potentially compromising sensitive information and posing a significant risk to national and economic security.
Ransomware Attacks

In the prevailing cyber landscape, businesses in Kenya are grappling with an escalating wave of ransomware attacks, characterized by a marked increase in successful breaches orchestrated by a range of threat actors from December 12, 2023, to March 1, 2024. Of alarm is the pronounced surge on February 10th, which recorded a substantial 550 successful ransomware infiltrations. This stark reality underscores the pressing necessity for bolstered cybersecurity fortifications to mitigate the profound implications these threats pose to business continuity, data security, financial stability, and overall operational resilience.
Such incidents not only jeopardize sensitive information but also erode consumer trust, disrupt critical services, and inflict enduring reputational damage on the affected organizations. Amidst these adversities, it is imperative for enterprises to urgently prioritize and implement comprehensive cybersecurity strategies to safeguard against the proliferating menace of ransomware assaults and ensure the sustained viability of their operations in an increasingly digital landscape.
Attack on emails
In a concerning trend, Kenya is experiencing a surge in email compromises, with an average of 250 email addresses falling victim to cyber attacks daily. When hackers gain access to an email account, the repercussions are severe. They can exploit this access to craft convincing phishing emails targeting network contacts. Successful phishing attacks pave the way for threat actors to infiltrate critical infrastructure and sensitive data, move laterally within systems, exfiltrate valuable information, and encrypt data, ultimately leading to ransom demands.
This alarming scenario underscores the critical need for organizations to bolster their cybersecurity measures, enhance vigilance, and address email security vulnerabilities promptly to mitigate the risks of devastating breaches and protect the integrity of their digital assets.
Criminal Network
Avalanche criminal syndicate which was brought down through international security cooperation in 2016 has re-emerge, present in Africa and very active in Kenya. The criminals harvest banks and email passwords, through their efficient phishing attacks. The group was first investigated in 2012 in Germany after they carried out a ransomware attack which had a devasting impact to significant amount of computer systems in Germany. Data collected for only one week of activity of the avalanche criminal network shows an average of 7 000 malware attacks in the first week of March 2024.
Attacks on web servers
A consistent onslaught is observed on vital business infrastructure in Kenya, particularly targeting web servers containing sensitive data. Throughout February 2024 to early March 2024, an average of 200 daily attacks were recorded on these web servers. This sustained threat underscores the critical necessity for comprehensive security solutions and proactive defense mechanisms to ensure the protection of crucial business information.
Attacks on wireless network
The wireless network Cambium has become a prime target for threat actors in Kenya. These assailants are consistently breaching broadband and Wi-Fi infrastructure, with an average of 150 daily attacks. This persistent threat underscores the critical need for robust security measures and comprehensive protocols to effectively mitigate and counter these malicious intrusions.
Attack on Telecommunication software
In Kenya, the communication software 3CX finds itself besieged by a wave of attacks of critical severity. Between December 2023 and March 2024, the software endured a staggering daily onslaught of 1000 attacks, painting a grim picture of the relentless assault on its vulnerabilities. These sustained attacks underscore the high stakes involved, highlighting the urgent need for enhanced security measures to safeguard the integrity and functionality of 3CX amidst the escalating cyber threats. As the software battles against this barrage of incursions, the period serves as a stark reminder of the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity challenges faced by modern communication systems.
Attack on HTTP Server Authentication
This authentication process involves the server soliciting user ID and password information. Daily, businesses are experiencing an average of 1000 compromises related to basic authentication. This underscores the imperative for comprehensive security strategies and heightened vigilance to effectively address and mitigate these security challenges.
Android SMS attacks
Kenya is facing a significant surge in Android SMS attacks, with an average of 1000 attacks occurring daily. This alarming trend poses severe implications for both individual users and organizational networks across the country.
The implications of these daily attacks are far-reaching and potentially devasting. Android SMS attacks can lead to unauthorized access to personal and sensitive information, financial data theft, and even the compromise of critical systems and infrastructure.
Given the escalating frequency and sophistication of Android SMS attacks in Kenya, proactive cybersecurity measures and heightened vigilance are essential to safeguard personal and organizational data, protect digital assets, and preserve the integrity of the country’s digital ecosystem.
Compromised Websites
In the heart of Kenya’s bustling digital landscape, over 100 websites fall victim to cyber compromises daily. This alarming trend not only jeopardizes the online presence of businesses but also undermines the trust and integrity of Kenya’s digital economy.
Kenya, a burgeoning hub of innovation and entrepreneurship, is witnessing a surge in cyber-attacks that target businesses of all sizes. From e-commerce platforms to financial institutions, no sector is immune to the perils of cyber vulnerabilities.
Safeguarding sensitive information, fortifying digital infrastructures, and implementing proactive threat detection mechanisms are essential steps in mitigating cyber risks.
Embracing a cybersecurity-first mindset is not just a matter of compliance; it’s a strategic imperative for businesses looking to thrive in the digital age. By prioritizing cybersecurity investments, organizations can safeguard their operations, protect their customers, and bolster the resilience of Kenya’s digital ecosystem.
Hardware implant attacks
The graph below illustrates a concerning trend of escalating attacks on computer systems, notably highlighting the prevalence of hardware implant attacks. These sophisticated tactics are being deployed by malicious actors to manipulate vulnerable IoT devices, compelling them to establish static IP addresses that serve as backdoors for unauthorized remote access. Notably, Kenya is experiencing a daily average of 250 such attacks. This insidious form of cyber threat demands heightened vigilance and robust cybersecurity protocols to safeguard against unauthorized intrusions.
Click here to read Part 2 of 2: Cyber Threat Landscape in Kenya: Trends and Solution
Obase Mandi Manga is the Cyber Security Engineer, HackProof Hub www.hackproofhub.au Email: mandi@hackproofhub.au